Understanding home insurance
home insurance Home insurance, also known as home owner’s insurance, is a type of property insurance that covers various risks to your home and its contents. fire, theft destruction Provides financial protection against risks such as natural disasters and liability claims.
Components covered:
Home insurance typically includes several key components:
a Living coverage: walls; the roof Protects your home’s structure, including floors and attached structures.
b Personal Property Coverage: Furniture; Covers your personal belongings, such as electronics and clothing.
c. Liability coverage: Provides financial protection if you are found legally liable if someone is injured on your property.
d. Additional Living Expenses Cover: Covers temporary living expenses if your home becomes uninhabitable due to an incident.
Types of home insurance policies:
including the types of home insurance policies available;
a HO-3 policy: The most common type that provides comprehensive coverage for structures and personal property, excluding specific exclusions.
b HO-5 Policy: Offers a wider range of risks, including protection for personal property.
c. HO-6 Policy: Designed for condominium owners to cover personal property and the interior of the unit.
d. HO-4 Policy: Especially Personal Property and Liability;
Additional coverage options:
Home insurance policies sometimes Allows for additional coverage options such as:
a Flood Insurance: Protection against flood damage, usually purchased as a separate policy.
b Earthquake Insurance: Covers damage caused by earthquakes, especially in high-risk areas.
c. Personal Liability Umbrella Policy: Provides additional liability coverage beyond the limits of your standard policy.
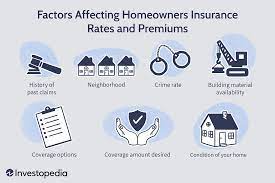
Factors affecting home insurance premiums:
A variety of factors can influence home insurance premiums, including:
a Location: Where your home is located, including coastal or disaster-prone areas.
b Construction and Age of Home: The materials used in construction and the age of your home can affect premium values.
c. Security measures: security systems; Installing smoke detectors and fire alarms can lower your premiums.
d. Claim History: A history of previous insurance claims can affect your premium rates.
Deductible Policy and Limits:
The deductible is the amount you pay out of pocket before your insurance coverage begins. Higher deductibles often result in lower premium rates. Policy limits refer to the maximum amount your insurance company will pay for a covered claim. When choosing a home insurance policy, it is important to understand the deductible and policy limits.
Running a home inventory:
Creating a detailed home inventory is critical to accurately assessing the value of your property. photos, Documenting your items, including receipts and descriptions, can speed up the claims process and ensure proper reimbursement in the event of loss.
Reviewing and updating your policy:
Regularly review and update your home insurance policy to ensure it meets your current needs. modification; You should notify your insurer of any changes, such as the acquisition of expensive items or changes in residence. This ensures that your coverage is adequate and up-to-date.
Comparing Insurance Providers:
When choosing a home insurance policy, compare offers from different insurance providers. coverage; premiums; Consider factors such as customer service reputation and the company’s financial stability. This comparison allows you to choose a reputable service provider that meets your specific needs.
Get professional advice:
If you have complex insurance needs or need help choosing the right policy, consult an insurance agent or broker. They can provide expert guidance, inform you of available options and help you make a decision.